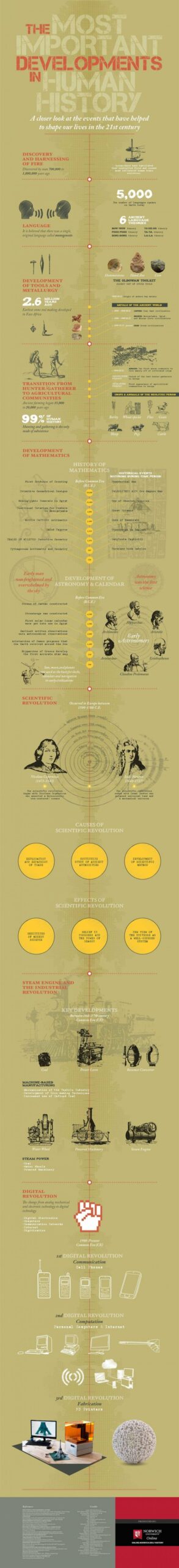
Introduction
Definition of development history
Development history refers to significant changes in economic, social, political, and cultural conditions that have affected large groups of people. It encompasses the actual historical and material occurrences that have shaped societies over time.
Importance of studying development history
Studying development history is crucial for several reasons:
1. Understanding the past: By examining the historical trajectory of development, we can gain insights into the factors that have contributed to societal progress and change. It allows us to learn from the successes and failures of the past.
2. Informing policy decisions: Knowledge of development history provides policymakers with a context for formulating effective strategies and policies. By understanding how development has occurred in the past, policymakers can make informed decisions to promote sustainable development in the present and future.
3. Identifying patterns and trends: Studying development history helps us identify patterns and trends that can inform our understanding of current development processes. It allows us to identify similarities and differences across regions and time periods, enabling us to discern recurring themes and challenges.
4. Challenging Western-centric perspectives: Development history offers an opportunity to critically examine the dominant Western concept of development as progress. By studying diverse historical experiences, we can challenge ethnocentric views, broaden our understanding of development, and promote more inclusive approaches.
5. Enriching interdisciplinary research: Development history draws upon various disciplines, including economics, sociology, political science, and cultural studies. It provides a rich source of interdisciplinary research, allowing scholars to explore the complex interactions between economic, social, political, and cultural factors in shaping development.
In conclusion, studying development history is essential for gaining a comprehensive understanding of societal progress and change. It provides valuable insights that can inform policy decisions, challenge Western-centric perspectives, identify patterns and trends, and enrich interdisciplinary research. By analyzing the past, we can better navigate the complexities of the present and work towards a more sustainable and inclusive future.
Pre-19th Century Development
Actual historical and material occurrences
In the late 19th century, there was a prevailing belief among historians that history could be transformed into a scientific discipline through the establishment of an exact process. However, it became clear that it was not possible to simply plug historical evidence into an equation and derive an absolute truth. Nonetheless, historians recognized the need for improving the process of historical methodology and began to establish some guidelines for it.
During this time, a variety of historians made significant efforts to develop and refine the process of historical methodology. For example, in the field of clinical medicine, scholars explored the principles that would later become foundational to 21st-century clinical pharmacology. Their work aimed to identify ways to effectively search for truth in clinical medicine, contributing to the development of evidence-based practices.
Lack of explicit theories and prescriptions
While historians in the late 19th century were motivated to enhance the process of historical methodology, there was a lack of explicit theories and prescriptions to guide their work. The notion of turning history into a science faced challenges as history deals with complex and multifaceted human experiences that cannot be easily reduced to an exact formula. Historians grappled with the inherent subjectivity and interpretative nature of their discipline.
Furthermore, the origins of evidence-based medicine can be traced back to different cultures and time periods. Some argue that it finds its roots in ancient Greek medicine, while others attribute its beginnings to ancient Chinese medicine. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that the effort to test medical interventions for efficacy evolved and began to impact a wide range of healthcare fields and policies.
In conclusion, the late 19th century marked a significant period of exploration and refinement in historical methodology. Historians recognized the need to improve the scientific aspects of their discipline and made efforts to establish guidelines for historical research. However, the complexity of history and the absence of explicit theories and prescriptions posed challenges in the pursuit of an exact process. The development of evidence-based medicine also underwent a gradual evolution, with origins that can be traced back to different cultures and time periods.
Theories of Development
Introduction of explicit theories in the mid-19th century
During the mid-19th century, there was a shift in the understanding of development, with the introduction of explicit theories that sought to explain the process of societal and individual progress. Prior to this period, development occurred without these explicit theories, making it difficult to analyze and understand the factors contributing to growth.
Theories of development emerged from various disciplines, including psychology, biology, and sociology. Psychodynamic theories, proposed by thinkers like Sigmund Freud, focused on the influence of unconscious desires and early childhood experiences on development. Behavioral theories, on the other hand, emphasized the impact of environmental stimuli and reinforcement on human behavior. Cognitive theories emphasized the role of mental processes such as perception, memory, and reasoning in development. Humanistic theories highlighted the importance of self-actualization and personal growth. Evolutionary theories drew inspiration from Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution and applied it to the study of human development.
Evolution of the concept of development as progress
The introduction of explicit theories of development in the mid-19th century also led to the evolution of the concept of development itself. Prior to this period, development was largely seen as a historical and material occurrence, involving significant changes in economic, social, political, and cultural conditions affecting large groups of people. However, with the advent of explicit theories, development started to be conceptualized as progress towards desired goals or outcomes.
This shift in the concept of development can be seen in the emergence of development assistance programs and the focus on sustainable livelihoods. Development assistance programs, such as those implemented by international organizations, aimed to promote economic, social, and political development in less developed countries. The goal was to help these countries achieve a higher level of development and improve the well-being of their citizens.
Sustainable livelihoods, on the other hand, emphasized the importance of long-term development that meets the needs of present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This approach recognizes the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors in achieving sustainable development.
In conclusion, the mid-19th century marked the introduction of explicit theories of development, which led to a shift in the understanding of development as progress towards desired goals or outcomes. These theories, rooted in various disciplines, provided frameworks for analyzing and understanding the factors influencing development. Additionally, the concept of development evolved to include the focus on sustainable livelihoods and the implementation of development assistance programs. These developments have influenced the way development is studied and approached in contemporary times.
Political Development
Historical and material changes in political conditions
Throughout history, political conditions have undergone significant changes that have shaped the course of societies. These changes can be attributed to a variety of factors, including economic developments, social transformations, and the struggle between different social classes. In the context of historical materialism, political development is closely intertwined with the underlying economic base.
In the late 19th century, there was a growing recognition among historians that political development could not be fully understood without considering its relationship with the economic base. Karl Marx’s theory of historical materialism argued that the evolution of society was driven by the class struggle rooted in the economic structure. According to Marx, as the productive forces of society developed, the existing political order became increasingly inadequate, leading to conflicts and the rise of new political systems.
The growth of agriculture played a crucial role in shaping political conditions throughout history. As agriculture advanced, larger groups emerged, giving rise to new challenges for social organization. This led to the formation of complex political structures that sought to address these challenges and maintain social order. For example, the development of irrigation systems in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt necessitated centralized political authority to manage the distribution of water and ensure the survival of agricultural communities.
Impact on large groups of people
The political development resulting from historical materialism had significant implications for large groups of people. The struggle between social classes and the changing economic base often resulted in conflicts and revolutions that aimed to transform political systems and address socio-economic inequalities.
One of the key implications of historical materialism was the recognition that historical change was not predetermined or driven by supernatural forces. Instead, it emphasized the role of human agency and class struggle in shaping political conditions. This challenged the prevailing notion that history was simply a series of accidents or the result of divine intervention.
The elevation of class consciousness and the organization of the working class became important drivers of political development. As workers became aware of their exploitation and organized themselves, they gained the power to challenge the existing political order and demand social and economic reforms. This led to the emergence of labor movements and the demand for workers’ rights, ultimately shaping the political landscape in many societies.
In summary, historical materialism highlights the intricate relationship between political development and the underlying economic base. The growth of agriculture and the emergence of larger social groups have influenced the formation of political structures throughout history. The recognition of the role of class struggle and human agency in shaping political conditions has had profound implications for large groups of people, leading to revolutions, social reforms, and the demand for workers’ rights. The understanding provided by historical materialism has revolutionized the study of history and challenged previous notions of the underlying causes of societal change.
Development Assistance
Role of development assistance in promoting change
Development assistance plays a crucial role in promoting change and addressing the economic and social challenges faced by developing countries. It refers to the aid provided by governments and international institutions to support the development and welfare of these nations. Development assistance aims to alleviate poverty, improve education and healthcare systems, and promote sustainable economic growth.
One of the primary goals of development assistance is to provide financial resources and technical expertise to developing countries. This assistance enables these nations to invest in infrastructure, such as transportation networks and energy systems, which are fundamental for economic growth. Additionally, development assistance can fund educational programs, healthcare initiatives, and social welfare projects, empowering individuals and communities to improve their living conditions.
Development assistance is not limited to financial aid. It also encompasses capacity building initiatives and knowledge transfer. Through technical assistance and training programs, developing countries can acquire the skills and knowledge necessary for sustainable economic development. This includes expertise in areas such as agriculture, renewable energy, and entrepreneurship, which can facilitate job creation and income generation.
It is crucial to note that development assistance should be tailored to the specific needs and priorities of each country. It should be based on a thorough understanding of local contexts, taking into account cultural, political, and social factors. Effective development assistance requires a collaborative approach, involving close cooperation between donor countries, international organizations, and recipient nations.
Sustainable livelihood and the Latin American study
Promoting sustainable livelihood is a key objective of development assistance. It involves ensuring that individuals and communities have the resources, capabilities, and opportunities to achieve a decent standard of living. Sustainable livelihood approaches recognize the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors, aiming to foster resilience and reduce vulnerability.
Latin America has been an important region for the study of sustainable livelihoods. The diversity of ecosystems, natural resources, and cultures in this region presents unique challenges and opportunities. Scholars and practitioners have focused on understanding the complex dynamics between economic development, social inclusion, and environmental conservation in Latin American countries.
In the Latin American study of sustainable livelihoods, various approaches have been used. These include participatory methods, which involve engaging local communities in the development process, and the identification of sustainable livelihood strategies that are context-specific. The study also emphasizes the importance of promoting gender equality, social justice, and the empowerment of marginalized groups.
Furthermore, sustainable livelihood approaches highlight the need for integrated and holistic development strategies. This includes promoting sustainable agriculture practices, supporting small-scale enterprises, and investing in renewable energy. By adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses economic, social, and environmental dimensions, development assistance can contribute to long-term sustainable development in Latin America and other regions.
In conclusion, development assistance plays a vital role in promoting change and addressing the challenges faced by developing countries. Through financial resources, capacity building initiatives, and knowledge transfer, development assistance empowers individuals and communities to achieve sustainable livelihoods. The Latin American study of sustainable livelihoods demonstrates the importance of a holistic approach that considers economic, social, and environmental factors. By working collaboratively and tailoring assistance to local contexts, development efforts can contribute to long-term positive change and improved living conditions.
Development Decade
The Development Decade refers to a specific period of time during which the international community focused on promoting and addressing various issues related to development. These development decades were characterized by key focus areas, initiatives, and goals established by the United Nations to drive progress in global development. Two significant development decades were the 1960-1970 1st Development Decade and the 1981-1990 3rd Development Decade. Let’s explore the key focus areas, achievements, and challenges faced during these two development decades.
Key focus areas during the development decade
During the 1960-1970 1st Development Decade, the international community aimed to address issues related to economic growth, poverty reduction, and education. The focus areas included:
– Promoting economic development and industrialization: Efforts were made to promote economic growth in developing countries through industrialization and the diversification of their economies.
– Reducing poverty and inequality: Strategies were implemented to minimize poverty and reduce income inequality to improve the quality of life for the most vulnerable populations.
– Enhancing education and human resources development: Emphasis was placed on improving access to quality education and developing human resources to enhance productivity and promote socio-economic development.
In the 1981-1990 3rd Development Decade, the focus areas were adjusted to reflect the changing global context. The key focus areas included:
– Sustainable development: The international community recognized the importance of sustainable development and adopted strategies to balance economic growth with environmental protection and social well-being.
– Gender equality and women’s empowerment: Efforts were made to address gender inequalities and promote women’s rights and empowerment in areas such as education, employment, and political participation.
– Technology transfer and capacity building: Initiatives were implemented to facilitate the transfer of technology to developing countries and enhance their capacity to harness technological advancements for development purposes.
Achievements and challenges faced
During the 1960-1970 1st Development Decade, significant achievements were made in terms of economic growth and poverty reduction. Many countries experienced substantial economic progress, with increased production and improved living standards. However, challenges such as persistent poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and social inequality remained prevalent.
In the 1981-1990 3rd Development Decade, progress was made in areas such as gender equality, environmental sustainability, and technology transfer. Efforts to promote gender equality led to increased women’s participation in decision-making processes and improved access to education and healthcare. Additionally, initiatives to promote sustainable development contributed to greater awareness of environmental issues and the adoption of environmentally-friendly practices. However, challenges such as limited financial resources, political instability, and conflicts impeded progress in many regions.
In conclusion, the Development Decades were pivotal periods during which the international community focused on addressing key development issues. The 1960-1970 1st Development Decade mainly targeted economic growth, poverty reduction, and education, while the 1981-1990 3rd Development Decade adjusted its focus to include sustainable development, gender equality, and technology transfer. Despite achievements in various areas, challenges such as poverty, inequality, and limited resources continue to pose obstacles to global development efforts.
Development and Culture
Influence of development on social and cultural conditions
The process of development has a significant impact on social and cultural conditions within a society. As societies progress and develop, they experience changes in various aspects of their culture, such as values, beliefs, traditions, and social norms. These changes are often influenced by factors such as economic growth, technological advancements, urbanization, and globalization. Here are some key ways in which development influences social and cultural conditions:
1. **Changing values and beliefs**: Economic development and modernization often lead to shifts in values and beliefs within a society. As societies become more economically prosperous, traditional cultural values may be challenged or replaced by new ones. For example, the emphasis on individualism and materialism may increase, leading to changes in social relationships and priorities.
2. **Adoption of new technologies**: Technological advancements play a significant role in shaping cultural practices. The adoption of new technologies, such as smartphones and social media, can influence the way people communicate, interact, and express themselves. This, in turn, impacts social norms, language, and traditional forms of communication.
3. **Urbanization and migration**: The process of urbanization and migration often results in the blending of diverse cultures. As people from different backgrounds come together in urban areas, cultural exchange and hybridization occur. This can lead to the emergence of new cultural practices, languages, and identities.
4. **Globalization**: Globalization has enabled the flow of ideas, information, and cultural products across borders. As a result, cultural influences from around the world have become more accessible, leading to the spread of certain cultural practices and the erosion of others. Globalization also brings about cultural diversity, as people from different cultures interact and influence each other.
Cultural implications of significant changes
Significant changes resulting from development can have both positive and negative implications for culture. Here are some examples:
1. **Loss of cultural traditions**: As societies go through rapid changes, traditional cultural practices and knowledge may be at risk of being lost or marginalized. This loss can have negative effects on communities, as it may erode their sense of identity and cohesion.
2. **Cultural homogenization**: Globalization and the adoption of Western cultural values can lead to a certain degree of cultural homogenization, where diverse cultural practices become less prevalent. This can result in the loss of cultural diversity and contribute to the dominance of a few dominant cultures.
3. **Cultural revitalization**: On the other hand, development can also provide opportunities for cultural revitalization and preservation. As people become more aware of the value of their cultural heritage, efforts may be made to protect and revive traditional practices, languages, and art forms.
4. **Intercultural exchange**: Development can facilitate intercultural exchange and understanding. As societies become more connected, people have the opportunity to learn from and appreciate different cultures. This can lead to the enrichment of cultural diversity and the promotion of tolerance and inclusivity.
In conclusion, development and culture are interrelated, with development influencing social and cultural conditions and cultural changes shaping the development process. While development brings about significant changes, it is essential to consider the cultural implications and strive for a balance between progress and the preservation of cultural diversity and heritage.
Historical Perspectives on Development
Relationship between development and historical context
Development is not a static concept, but rather a reflection of the historical and material conditions of a society. It is influenced by the economic, social, political, and cultural changes that occur over time. The relationship between development and historical context can be understood in the following ways:
– Economic conditions: Development is closely linked to changes in economic activities and systems. For example, the shift from agrarian to industrial economies in the 18th and 19th centuries led to significant developments in production, infrastructure, and standards of living.
– Social transformations: Development is often accompanied by social changes, such as shifts in gender roles, social hierarchies, and cultural norms. These changes can impact the distribution of resources, access to education and healthcare, and overall quality of life.
– Political dynamics: Political factors play a crucial role in shaping development outcomes. The establishment of stable governance systems, the rule of law, and inclusive political institutions are essential for sustainable development. Similarly, political instability, corruption, and conflicts can hinder progress and perpetuate inequalities.
Understanding the historical context is essential for comprehending development processes and identifying the underlying factors that contribute to or impede progress.
Lessons learned from historical development experiences
Analyzing historical development experiences provides valuable insights into the approaches and strategies that have been successful or ineffective. Some key lessons learned include:
– Context-specific approach: Development interventions must consider the specific historical, cultural, and socioeconomic context of each society. There is no one-size-fits-all solution to development challenges. Tailoring strategies to local conditions enhances the effectiveness and sustainability of development initiatives.
– Holistic approach: Development should not focus solely on economic growth but also consider social and environmental dimensions. Sustainable development requires a balance between economic progress, social equity, and environmental preservation. Neglecting any of these aspects can undermine long-term development.
– Empowerment and participation: Inclusive development processes that empower individuals, communities, and marginalized groups are essential for sustainable progress. Ensuring their active participation in decision-making processes and providing opportunities for their economic and social advancement are crucial for reducing inequalities.
– Learning from failures: Failure is an inevitable part of the development process. It is important to acknowledge and learn from failures and adapt strategies accordingly. Reflecting on past mistakes helps avoid repeating them and promotes innovation and resilience in development efforts.
By examining historical development experiences, societies can gain valuable insights into what works and what doesn’t in promoting sustainable development. This knowledge can guide policymakers, practitioners, and communities in designing effective strategies and policies for the future.
In conclusion, historical perspectives on development reveal the intricate relationship between development and historical context. Economic, social, and political factors shape development outcomes, and lessons learned from past experiences can inform future strategies. Taking into account the specific context and adopting a holistic approach to development is crucial for achieving sustainable and inclusive progress.
Conclusion
Importance of understanding development history
Understanding the historical context of development is vital for comprehending the complexities of the subject. Development is not a static concept but is influenced by various factors that evolve over time. By studying the history of development, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the economic, social, political, and cultural changes that shape societies.
Developments in economic activities and systems have played a significant role in shaping the concept of development. For instance, the transition from agrarian to industrial economies in the 18th and 19th centuries led to advancements in production, infrastructure, and living standards. Understanding these economic shifts can provide insights into the factors that contribute to economic growth and societal progress.
Social transformations are also closely linked to development. Changes in gender roles, social hierarchies, and cultural norms have had an impact on resource distribution, access to education and healthcare, and overall quality of life. By studying historical development experiences, individuals can identify patterns and trends in social changes and their implications for development outcomes.
Political factors are crucial in shaping development outcomes as well. The establishment of stable governance systems, the rule of law, and inclusive political institutions are essential for sustainable development. Conversely, political instability, corruption, and conflicts can hinder progress and perpetuate inequalities. Examining historical experiences helps identify the political dynamics that facilitate or hinder development.
Future outlook and implications of development history
Analyzing historical development experiences provides valuable lessons that can guide future strategies. One important lesson is the need for a context-specific approach to development. While there are universal principles, such as human rights and social justice, each society is unique and requires tailored strategies that consider its historical, cultural, and socioeconomic context. This approach enhances the effectiveness and sustainability of development interventions.
A holistic approach to development is crucial for long-term progress. Economic growth should not be the sole focus, but rather a balance between economic, social, and environmental dimensions is necessary. Neglecting any of these aspects can lead to negative consequences and undermine sustainable development. By learning from historical experiences, policymakers can prioritize and address these different dimensions effectively.
Empowerment and participation are essential for inclusive development. Ensuring that individuals, communities, and marginalized groups are actively involved in decision-making processes and provided with opportunities for economic and social advancement can help reduce inequalities. Lessons from history emphasize the importance of empowering marginalized groups and promoting social justice in development efforts.
Furthermore, acknowledging and learning from failures is critical for progress. Reflecting on past mistakes and adapting strategies accordingly promotes innovation and resilience in development initiatives. By embracing a learning mindset, societies can avoid repeating past errors and constantly improve their approaches to development.
In conclusion, understanding development history is essential for comprehending the complex relationship between development and historical context. Economic, social, and political factors shape development outcomes, and learning from historical experiences helps guide future strategies. By taking into account the specific context, adopting a holistic approach, and prioritizing empowerment and participation, societies can strive towards sustainable and inclusive progress.